 Web Services Original
Web Services Original Web Services Original
Web Services Original
For the benefit of novices like myself, could someone please explain the above attributes, preferably with an example? In particular, 'dynamically composable'.
See a nice picture from http://www.service-architecture.com/index.html
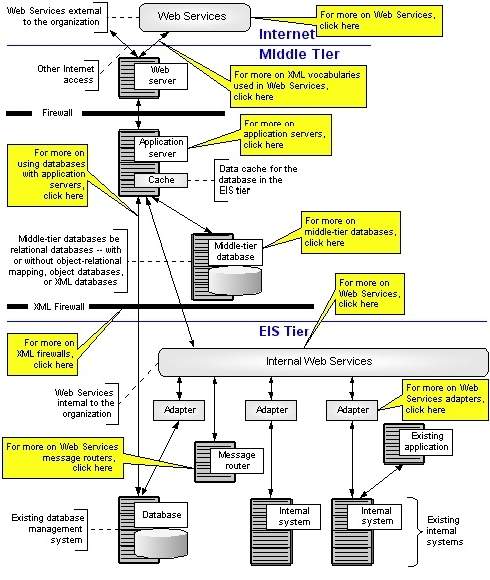
Comparisons with a SoaImplementationFramework inspired implementation?
In summary, Web services are effectively another attempt at solving the "holy grail" of DistributedComputing: a platform that will finally enable ubiquitous distributed components and composable systems to be written by average developers. Prior attempts have met with mixed results (some of which are Sun RPC, DCE RPC, DCOM, CORBA, and RMI).
"Many have tried." "They tried and failed?" "They tried and died." - Reverend Mother Helen Moah'im, Dune[Please leave comments to the end of the page]
WebServices under the influence of the dreaded Xml
WebServices are different in that the common data representation is XML, or more specifically, the XmlInfoSet. XML provides a standardized information set for specifying messages between software services, one that is independent of processing model. The text-based extensible markup language is the 'least common denominator' encoding method XmlInfoSet.
The effect of XML is to enable what is effectively a semantic data stream for all messages. SDS is a concept coined by OliverSims, but one that has a heritage in the LispLanguage (read StructureAndInterpretationOfComputerPrograms). SDS implies carrying the structure of the message (its metadata) along with the message, as opposed to completely relying on extrinsic definition of interface or data structure.
Carrying along this "metadata" is crucial to allow for loose coupling, dynamic binding and run-time interoperability.This is the key difference between the WebServices approach and previous approaches, which relied heavily on immutable interfaces, early binding, and/or high coupling to a particular platform or object model.
The other key aspect to WebServices is the simplicity of its architecture compared to former models. XmlSchema throws a fair amount of complexity into the mix, so this simplicity isn't guaranteed to last. In the short term, the higher bandwidth consumption of XML versus binary data representations is the primary trade-off made to achieve this simplicity. In the long term, binary encodings of the XmlInfoSet will enable high-performance WebServices.
The current specifications to enable Web services are:
Check out the list of organizations and consortia involved in WebServices at http://www.service-architecture.com/web-services/articles/organizations.html
WebServices for the REST of us
The most common transport protocol used will be HTTP, since it is ubiquitous and "firewall safe". Of course, the RealWorld will require differing levels of service or security, hence the perceived need for protocol independence.
An emerging debate about the shape of Web services is whether all these extra XML protocols and interfaces provide enough value in exchange for their complexity. The RestArchitecturalStyle is an alternative way of building Web services. Their premise is that HTTP in and of itself has the set of "verbs" (GET, POST, etc) we need to implement Web services. All we need new are lots of "nouns" (URIs).
A lot of big guys are making noise about Web services; currently the grassroots are doing the work of implementing real-world services.
The main competing implementations of XML WebServices engines are:
Examples http://www.eaves.org/google/howcool
Completely useless (or is it?) application using Google's WebServices API
Q Looking for a simplge way to wrap BigBlue functionality into RestArchitecturalStyle WebServices without using SoapProtocol offered in CiCs 2.2. We have DbTwo version 6
A
Q Any experiences related to WebServicesTesting?? -- RaghuHavaldar?
A
See WebServicesDiscussion, WebServicesDescriptionLanguage (WSDL), ServiceOrientedArchitecture
Interoperability aspects
BusinessProcessExecutionLanguageforWebServices (BPEL4WS or just BPEL) is meant to be an execution environment independent mechanism for long running conversions between organizations. However, there are efforts to have language specific extensions (e.g. BPELJ) that diminish interoperability. See http://www.theregister.co.uk/2004/03/24/ibm_moots_bpeljava_fusion/
UniversalBusinessLanguage (UBL) is another ExtensibleMarkupLanguage based specification intended to reduce communication barrier between applications through due to semantic variances. See http://searchwebservices.techtarget.com/originalContent/0,289142,sid26_gci970231,00.html
Both can be considered to be higher level WorkFlow activities.
Learning Resources
(Dru here - and yes, Web Services will die too. This technology completely ignores certain _unwritten_truths_ about internet technologies, and will end up being a huge, performance sucking monster. Lets see how long this stays here.)
All technologies die. The question is whether they provided value and paid the bills while they were alive. Thus far, WS are doing okay.. -- StuCharlton
Incidentally, asynchronous message patterns are a weakness of current web service specifications (WSDL) which assume that everything is a query-response or invoke-acknowledge one-shot interaction, rather than a two-way conversation. Agent-based systems have dealt with more complex conversation protocols for a long time now. -- DavidAllsopp
Reading material
See also: KissWebServices
 EditText of this page
(last edited July 17, 2006)
or FindPage with title or text search
EditText of this page
(last edited July 17, 2006)
or FindPage with title or text search